How Lua runs in HAProxy¶
HAProxy Lua running contexts¶
The Lua code executed in HAProxy can be processed in 2 main modes. The first one is the initialisation mode, and the second is the runtime mode.
In the initialisation mode, we can perform DNS solves, but we cannot perform socket I/O. In this initialisation mode, HAProxy still blocked during the execution of the Lua program.
In the runtime mode, we cannot perform DNS solves, but we can use sockets. The execution of the Lua code is multiplexed with the requests processing, so the Lua code seems to be run in blocking, but it is not the case.
The Lua code is loaded in one or more files. These files contains main code and functions. Lua have 6 execution context.
The Lua file body context. It is executed during the load of the Lua file in the HAProxy [global] section with the directive lua-load. It is executed in initialisation mode. This section is use for configuring Lua bindings in HAProxy.
The Lua init context. It is a Lua function executed just after the HAProxy configuration parsing. The execution is in initialisation mode. In this context the HAProxy environment are already initialized. It is useful to check configuration, or initializing socket connections or tasks. These functions are declared in the body context with the Lua function core.register_init(). The prototype of the function is a simple function without return value and without parameters, like this: function fcn().
The Lua task context. It is a Lua function executed after the start of the HAProxy scheduler, and just after the declaration of the task with the Lua function core.register_task(). This context can be concurrent with the traffic processing. It is executed in runtime mode. The prototype of the function is a simple function without return value and without parameters, like this: function fcn().
The action context. It is a Lua function conditionally executed. These actions are registered by the Lua directives “core.register_action()”. The prototype of the Lua called function is a function with doesn’t returns anything and that take an object of class TXN as entry. function fcn(txn).
The sample-fetch context. This function takes a TXN object as entry argument and returns a string. These types of function cannot execute any blocking function. They are useful to aggregate some of original HAProxy sample-fetches and return the result. The prototype of the function is function string fcn(txn). These functions can be registered with the Lua function core.register_fetches(). Each declared sample-fetch is prefixed by the string “lua.”.
NOTE: It is possible that this function cannot found the required data in the original HAProxy sample-fetches, in this case, it cannot return the result. This case is not yet supported
The converter context. It is a Lua function that takes a string as input and returns another string as output. These types of function are stateless, it cannot access to any context. They don’t execute any blocking function. The call prototype is function string fcn(string). This function can be registered with the Lua function core.register_converters(). Each declared converter is prefixed by the string “lua.”.
HAProxy Lua Hello world¶
HAProxy configuration file (hello_world.conf):
global
lua-load hello_world.lua
listen proxy
bind 127.0.0.1:10001
tcp-request inspect-delay 1s
tcp-request content use-service lua.hello_world
HAProxy Lua file (hello_world.lua):
core.register_service("hello_world", "tcp", function(applet)
applet:send("hello world\n")
end)
How to start HAProxy for testing this configuration:
./haproxy -f hello_world.conf
On other terminal, you can test with telnet:
#:~ telnet 127.0.0.1 10001
hello world
Core class¶
-
class
core()¶ The “core” class contains all the HAProxy core functions. These function are useful for the controlling the execution flow, registering hooks, manipulating global maps or ACL, …
“core” class is basically provided with HAProxy. No require line is required to uses these function.
The “core” class is static, it is not possible to create a new object of this type.
-
core.emerg¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “emergency” (0).
-
core.alert¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “alert” (1).
-
core.crit¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “critical” (2).
-
core.err¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “error” (3).
-
core.warning¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “warning” (4).
-
core.notice¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “notice” (5).
-
core.info¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “info” (6).
-
core.debug¶ - Returns
integer
This attribute is an integer, it contains the value of the loglevel “debug” (7).
-
core.proxies¶ context: task, action, sample-fetch, converter
This attribute is a table of declared proxies (frontend and backends). Each proxy give an access to his list of listeners and servers. The table is indexed by proxy name, and each entry is of type Proxy class.
Warning, if you are declared frontend and backend with the same name, only one of these are listed.
- See
- See
-
core.backends¶ context: task, action, sample-fetch, converter
This attribute is a table of declared proxies with backend capability. Each proxy give an access to his list of listeners and servers. The table is indexed by the backend name, and each entry is of type Proxy class.
- See
- See
-
core.frontends¶ context: task, action, sample-fetch, converter
This attribute is a table of declared proxies with frontend capability. Each proxy give an access to his list of listeners and servers. The table is indexed by the frontend name, and each entry is of type Proxy class.
- See
- See
-
core.log(loglevel, msg)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
This function sends a log. The log is sent, according with the HAProxy configuration file, on the default syslog server if it is configured and on the stderr if it is allowed.
- Arguments
loglevel (integer) – Is the log level associated with the message. It is a number between 0 and 7.
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
core.emerg,core.alert,core.crit,core.err,core.warning,core.notice,core.info,core.debug(log level definitions)- See
- See
- See
- See
-
core.Debug(msg)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
- Arguments
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
Does the same job than:
function Debug(msg)
core.log(core.debug, msg)
end
-
core.Info(msg)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
- Arguments
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
function Info(msg)
core.log(core.info, msg)
end
-
core.Warning(msg)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
- Arguments
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
function Warning(msg)
core.log(core.warning, msg)
end
-
core.Alert(msg)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
- Arguments
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
function Alert(msg)
core.log(core.alert, msg)
end
-
core.add_acl(filename, key)¶ context: init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Add the ACL key in the ACLs list referenced by the file filename.
- Arguments
filename (string) – the filename that reference the ACL entries.
key (string) – the key which will be added.
-
core.del_acl(filename, key)¶ context: init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Delete the ACL entry referenced by the key key in the list of ACLs referenced by filename.
- Arguments
filename (string) – the filename that reference the ACL entries.
key (string) – the key which will be deleted.
-
core.del_map(filename, key)¶ context: init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Delete the map entry indexed with the specified key in the list of maps referenced by his filename.
- Arguments
filename (string) – the filename that reference the map entries.
key (string) – the key which will be deleted.
-
core.get_info()¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Returns HAProxy core informations. We can found information like the uptime, the pid, memory pool usage, tasks number, …
These information are also returned by the management socket via the command “show info”. See the management socket documentation for more information about the content of these variables.
- Returns
an array of values.
-
core.now()¶ context: body, init, task, action
This function returns the current time. The time returned is fixed by the HAProxy core and assures than the hour will be monotonic and that the system call ‘gettimeofday’ will not be called too. The time is refreshed between each Lua execution or resume, so two consecutive call to the function “now” will probably returns the same result.
- Returns
a table which contains two entries “sec” and “usec”. “sec” contains the current at the epoch format, and “usec” contains the current microseconds.
-
core.http_date(date)¶ context: body, init, task, action
This function take a string representing http date, and returns an integer containing the corresponding date with a epoch format. A valid http date me respect the format IMF, RFC850 or ASCTIME.
- Arguments
date (string) – a date http-date formatted
- Returns
integer containing epoch date
- See
- See
- See
- See
-
core.imf_date(date)¶ context: body, init, task, action
This function take a string representing IMF date, and returns an integer containing the corresponding date with a epoch format.
- Arguments
date (string) – a date IMF formatted
- Returns
integer containing epoch date
- See
The IMF format is like this:
Sun, 06 Nov 1994 08:49:37 GMT
-
core.rfc850_date(date)¶ context: body, init, task, action
This function take a string representing RFC850 date, and returns an integer containing the corresponding date with a epoch format.
- Arguments
date (string) – a date RFC859 formatted
- Returns
integer containing epoch date
- See
The RFC850 format is like this:
Sunday, 06-Nov-94 08:49:37 GMT
-
core.asctime_date(date)¶ context: body, init, task, action
This function take a string representing ASCTIME date, and returns an integer containing the corresponding date with a epoch format.
- Arguments
date (string) – a date ASCTIME formatted
- Returns
integer containing epoch date
- See
The ASCTIME format is like this:
Sun Nov 6 08:49:37 1994
-
core.rfc850_date(date)¶ context: body, init, task, action
This function take a string representing http date, and returns an integer containing the corresponding date with a epoch format.
- Arguments
date (string) – a date http-date formatted
-
core.asctime_date(date)¶ context: body, init, task, action
This function take a string representing http date, and returns an integer containing the corresponding date with a epoch format.
- Arguments
date (string) – a date http-date formatted
-
core.msleep(milliseconds)¶ context: body, init, task, action
The core.msleep() stops the Lua execution between specified milliseconds.
- Arguments
milliseconds (integer) – the required milliseconds.
-
core.proxies¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Proxies is a table containing the list of all proxies declared in the configuration file. The table is indexed by the proxy name, and each entry of the proxies table is an object of type Proxy class.
Warning, if you have declared a frontend and backend with the same name, only one of these are listed.
-
core.register_action(name, actions, func[, nb_args])¶ context: body
Register a Lua function executed as action. All the registered action can be used in HAProxy with the prefix “lua.”. An action gets a TXN object class as input.
- Arguments
name (string) – is the name of the converter.
actions (table) – is a table of string describing the HAProxy actions who want to register to. The expected actions are ‘tcp-req’, ‘tcp-res’, ‘http-req’ or ‘http-res’.
nb_args (integer) – is the expected number of argument for the action. By default the value is 0.
func (function) – is the Lua function called to work as converter.
The prototype of the Lua function used as argument is:
function(txn [, arg1 [, arg2]])
- txn (TXN class): this is a TXN object used for manipulating the
current request or TCP stream.
argX: this is argument provided through the HAProxy configuration file.
Here, an example of action registration. The action just send an ‘Hello world’ in the logs.
core.register_action("hello-world", { "tcp-req", "http-req" }, function(txn)
txn:Info("Hello world")
end)
This example code is used in HAproxy configuration like this:
frontend tcp_frt
mode tcp
tcp-request content lua.hello-world
frontend http_frt
mode http
http-request lua.hello-world
A second example using arguments
function hello_world(txn, arg)
txn:Info("Hello world for " .. arg)
end
core.register_action("hello-world", { "tcp-req", "http-req" }, hello_world, 2)
This example code is used in HAproxy configuration like this:
frontend tcp_frt
mode tcp
tcp-request content lua.hello-world everybody
-
core.register_converters(name, func)¶ context: body
Register a Lua function executed as converter. All the registered converters can be used in HAProxy with the prefix “lua.”. An converter get a string as input and return a string as output. The registered function can take up to 9 values as parameter. All the value are strings.
- Arguments
name (string) – is the name of the converter.
func (function) – is the Lua function called to work as converter.
The prototype of the Lua function used as argument is:
function(str, [p1 [, p2 [, ... [, p5]]]])
str (string): this is the input value automatically converted in string.
p1 .. p5 (string): this is a list of string arguments declared in the HAProxy configuration file. The number of arguments doesn’t exceed 5. The order and the nature of these is conventionally choose by the developer.
-
core.register_fetches(name, func)¶ context: body
Register a Lua function executed as sample fetch. All the registered sample fetch can be used in HAProxy with the prefix “lua.”. A Lua sample fetch return a string as output. The registered function can take up to 9 values as parameter. All the value are strings.
- Arguments
name (string) – is the name of the converter.
func (function) – is the Lua function called to work as sample fetch.
The prototype of the Lua function used as argument is:
string function(txn, [p1 [, p2 [, ... [, p5]]]])
txn (TXN class): this is the txn object associated with the current request.
p1 .. p5 (string): this is a list of string arguments declared in the HAProxy configuration file. The number of arguments doesn’t exceed 5. The order and the nature of these is conventionally choose by the developer.
Returns: A string containing some data, or nil if the value cannot be returned now.
lua example code:
core.register_fetches("hello", function(txn)
return "hello"
end)
HAProxy example configuration:
frontend example
http-request redirect location /%[lua.hello]
-
core.register_service(name, mode, func)¶ context: body
Register a Lua function executed as a service. All the registered service can be used in HAProxy with the prefix “lua.”. A service gets an object class as input according with the required mode.
- Arguments
name (string) – is the name of the converter.
mode (string) – is string describing the required mode. Only ‘tcp’ or ‘http’ are allowed.
func (function) – is the Lua function called to work as converter.
The prototype of the Lua function used as argument is:
function(applet)
applet applet will be a AppletTCP class or a AppletHTTP class. It depends the type of registered applet. An applet registered with the ‘http’ value for the mode parameter will gets a AppletHTTP class. If the mode value is ‘tcp’, the applet will gets a AppletTCP class.
warning: Applets of type ‘http’ cannot be called from ‘tcp-‘ rulesets. Only the ‘http-‘ rulesets are authorized, this means that is not possible to call an HTTP applet from a proxy in tcp mode. Applets of type ‘tcp’ can be called from anywhere.
Here, an example of service registration. The service just send an ‘Hello world’ as an http response.
core.register_service("hello-world", "http", function(applet)
local response = "Hello World !"
applet:set_status(200)
applet:add_header("content-length", string.len(response))
applet:add_header("content-type", "text/plain")
applet:start_response()
applet:send(response)
end)
This example code is used in HAproxy configuration like this:
frontend example
http-request use-service lua.hello-world
-
core.register_init(func)¶ context: body
Register a function executed after the configuration parsing. This is useful to check any parameters.
- Arguments
func (function) – is the Lua function called to work as initializer.
The prototype of the Lua function used as argument is:
function()
It takes no input, and no output is expected.
-
core.register_task(func)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Register and start independent task. The task is started when the HAProxy main scheduler starts. For example this type of tasks can be executed to perform complex health checks.
- Arguments
func (function) – is the Lua function called to work as initializer.
The prototype of the Lua function used as argument is:
function()
It takes no input, and no output is expected.
-
core.register_cli([path, ]usage, func)¶ context: body
Register and start independent task. The task is started when the HAProxy main scheduler starts. For example this type of tasks can be executed to perform complex health checks.
- Arguments
path (array) – is the sequence of word for which the cli execute the Lua binding.
usage (string) – is the usage message displayed in the help.
func (function) – is the Lua function called to handle the CLI commands.
The prototype of the Lua function used as argument is:
function(AppletTCP, [arg1, [arg2, [...]]])
I/O are managed with the AppletTCP class object. Args are given as parameter. The args embed the registered path. If the path is declared like this:
core.register_cli({"show", "ssl", "stats"}, "Display SSL stats..", function(applet, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4, arg5)
end)
And we execute this in the prompt:
> prompt
> show ssl stats all
Then, arg1, arg2 and arg3 will contains respectively “show”, “ssl” and “stats”. arg4 will contain “all”. arg5 contains nil.
-
core.set_nice(nice)¶ context: task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Change the nice of the current task or current session.
- Arguments
nice (integer) – the nice value, it must be between -1024 and 1024.
-
core.set_map(filename, key, value)¶ context: init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Set the value value associated to the key key in the map referenced by filename.
- Arguments
filename (string) – the Map reference
key (string) – the key to set or replace
value (string) – the associated value
-
core.sleep(int seconds)¶ context: body, init, task, action
The core.sleep() functions stop the Lua execution between specified seconds.
- Arguments
seconds (integer) – the required seconds.
-
core.tcp()¶ context: init, task, action
This function returns a new object of a socket class.
- Returns
A Socket class object.
-
core.concat()¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
This function returns a new concat object.
- Returns
A Concat class object.
-
core.done(data)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
- Arguments
data (any) – Return some data for the caller. It is useful with sample-fetches and sample-converters.
Immediately stops the current Lua execution and returns to the caller which may be a sample fetch, a converter or an action and returns the specified value (ignored for actions). It is used when the LUA process finishes its work and wants to give back the control to HAProxy without executing the remaining code. It can be seen as a multi-level “return”.
-
core.yield()¶ context: task, action, sample-fetch, converter
Give back the hand at the HAProxy scheduler. It is used when the LUA processing consumes a lot of processing time.
-
core.parse_addr(address)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
- Arguments
network – is a string describing an ipv4 or ipv6 address and optionally its network length, like this: “127.0.0.1/8” or “aaaa::1234/32”.
- Returns
a userdata containing network or nil if an error occurs.
Parse ipv4 or ipv6 addresses and its facultative associated network.
-
core.match_addr(addr1, addr2)¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
- Arguments
addr1 – is an address created with “core.parse_addr”.
addr2 – is an address created with “core.parse_addr”.
- Returns
boolean, true if the network of the addresses match, else returns false.
Match two networks. For example “127.0.0.1/32” matchs “127.0.0.0/8”. The order of network is not important.
-
core.tokenize(str, separators[, noblank])¶ context: body, init, task, action, sample-fetch, converter
This function is useful for tokenizing an entry, or splitting some messages. :param string str: The string which will be split. :param string separators: A string containing a list of separators. :param boolean noblank: Ignore empty entries. :returns: an array of string.
For example:
local array = core.tokenize("This function is useful, for tokenizing an entry.", "., ", true)
print_r(array)
Returns this array:
(table) table: 0x21c01e0 [
1: (string) "This"
2: (string) "function"
3: (string) "is"
4: (string) "useful"
5: (string) "for"
6: (string) "tokenizing"
7: (string) "an"
8: (string) "entry"
]
Proxy class¶
-
class
Proxy()¶ This class provides a way for manipulating proxy and retrieving information like statistics.
-
Proxy.name¶ Contain the name of the proxy.
-
Proxy.uuid¶ Contain the unique identifier of the proxy.
-
Proxy.servers¶ Contain a table with the attached servers. The table is indexed by server name, and each server entry is an object of type Server class.
-
Proxy.listeners¶ Contain a table with the attached listeners. The table is indexed by listener name, and each each listeners entry is an object of type Listener class.
-
Proxy.pause(px)¶ Pause the proxy. See the management socket documentation for more information.
- Arguments
px (class_proxy) – A Proxy class which indicates the manipulated proxy.
-
Proxy.resume(px)¶ Resume the proxy. See the management socket documentation for more information.
- Arguments
px (class_proxy) – A Proxy class which indicates the manipulated proxy.
-
Proxy.stop(px)¶ Stop the proxy. See the management socket documentation for more information.
- Arguments
px (class_proxy) – A Proxy class which indicates the manipulated proxy.
-
Proxy.shut_bcksess(px)¶ Kill the session attached to a backup server. See the management socket documentation for more information.
- Arguments
px (class_proxy) – A Proxy class which indicates the manipulated proxy.
-
Proxy.get_cap(px)¶ Returns a string describing the capabilities of the proxy.
- Arguments
px (class_proxy) – A Proxy class which indicates the manipulated proxy.
- Returns
a string “frontend”, “backend”, “proxy” or “ruleset”.
-
Proxy.get_mode(px)¶ Returns a string describing the mode of the current proxy.
- Arguments
px (class_proxy) – A Proxy class which indicates the manipulated proxy.
- Returns
a string “tcp”, “http”, “health” or “unknown”
-
Proxy.get_stats(px)¶ Returns a table containing the proxy statistics. The statistics returned are not the same if the proxy is frontend or a backend.
- Arguments
px (class_proxy) – A Proxy class which indicates the manipulated proxy.
- Returns
a key/value table containing stats
Server class¶
-
class
Server()¶ This class provides a way for manipulating servers and retrieving information.
-
Server.is_draining(sv)¶ Return true if the server is currently draining sticky connections.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
- Returns
a boolean
-
Server.set_weight(sv, weight)¶ Dynamically change the weight of the server. See the management socket documentation for more information about the format of the string.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
weight (string) – A string describing the server weight.
-
Server.get_weight(sv)¶ This function returns an integer representing the server weight.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
- Returns
an integer.
-
Server.set_addr(sv, addr)¶ Dynamically change the address of the server. See the management socket documentation for more information about the format of the string.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
addr (string) – A string describing the server address.
-
Server.get_addr(sv)¶ Returns a string describing the address of the server.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
- Returns
A string
-
Server.get_stats(sv)¶ Returns server statistics.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
- Returns
a key/value table containing stats
-
Server.shut_sess(sv)¶ Shutdown all the sessions attached to the server. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.set_drain(sv)¶ Drain sticky sessions. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.set_maint(sv)¶ Set maintenance mode. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.set_ready(sv)¶ Set normal mode. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.check_enable(sv)¶ Enable health checks. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.check_disable(sv)¶ Disable health checks. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.check_force_up(sv)¶ Force health-check up. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.check_force_nolb(sv)¶ Force health-check nolb mode. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.check_force_down(sv)¶ Force health-check down. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.agent_enable(sv)¶ Enable agent check. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.agent_disable(sv)¶ Disable agent check. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.agent_force_up(sv)¶ Force agent check up. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
-
Server.agent_force_down(sv)¶ Force agent check down. See the management socket documentation for more information about this function.
- Arguments
sv (class_server) – A Server class which indicates the manipulated server.
Listener class¶
-
Listener.get_stats(ls)¶ Returns server statistics.
- Arguments
ls (class_listener) – A Listener class which indicates the manipulated listener.
- Returns
a key/value table containing stats
Concat class¶
-
class
Concat()¶ This class provides a fast way for string concatenation. The way using native Lua concatenation like the code below is slow for some reasons.
str = "string1"
str = str .. ", string2"
str = str .. ", string3"
For each concatenation, Lua: * allocate memory for the result, * catenate the two string copying the strings in the new memory bloc, * free the old memory block containing the string which is no longer used. This process does many memory move, allocation and free. In addition, the memory is not really freed, it is just mark mark as unused and wait for the garbage collector.
The Concat class provide an alternative way to concatenate strings. It uses the internal Lua mechanism (it does not allocate memory), but it doesn’t copy the data more than once.
On my computer, the following loops spends 0.2s for the Concat method and 18.5s for the pure Lua implementation. So, the Concat class is about 1000x faster than the embedded solution.
for j = 1, 100 do
c = core.concat()
for i = 1, 20000 do
c:add("#####")
end
end
for j = 1, 100 do
c = ""
for i = 1, 20000 do
c = c .. "#####"
end
end
-
Concat.add(concat, string)¶ This function adds a string to the current concatenated string.
- Arguments
concat (class_concat) – A Concat class which contains the currently builded string.
string (string) – A new string to concatenate to the current built string.
-
Concat.dump(concat)¶ This function returns the concatenated string.
- Arguments
concat (class_concat) – A Concat class which contains the currently builded string.
- Returns
the concatenated string
Fetches class¶
-
class
Fetches()¶ This class contains a lot of internal HAProxy sample fetches. See the HAProxy “configuration.txt” documentation for more information about her usage. They are the chapters 7.3.2 to 7.3.6.
warning some sample fetches are not available in some context. These limitations are specified in this documentation when they’re useful.
Fetches are useful for:
get system time,
get environment variable,
get random numbers,
known backend status like the number of users in queue or the number of connections established,
client information like ip source or destination,
deal with stick tables,
Established SSL informations,
HTTP information like headers or method.
function action(txn)
-- Get source IP
local clientip = txn.f:src()
end
Converters class¶
-
class
Converters()¶ This class contains a lot of internal HAProxy sample converters. See the HAProxy documentation “configuration.txt” for more information about her usage. Its the chapter 7.3.1.
Converters provides statefull transformation. They are useful for:
converting input to base64,
applying hash on input string (djb2, crc32, sdbm, wt6),
format date,
json escape,
extracting preferred language comparing two lists,
turn to lower or upper chars,
deal with stick tables.
Channel class¶
-
class
Channel()¶ HAProxy uses two buffers for the processing of the requests. The first one is used with the request data (from the client to the server) and the second is used for the response data (from the server to the client).
Each buffer contains two types of data. The first type is the incoming data waiting for a processing. The second part is the outgoing data already processed. Usually, the incoming data is processed, after it is tagged as outgoing data, and finally it is sent. The following functions provides tools for manipulating these data in a buffer.
The following diagram shows where the channel class function are applied.
Warning: It is not possible to read from the response in request action, and it is not possible to read for the request channel in response action.
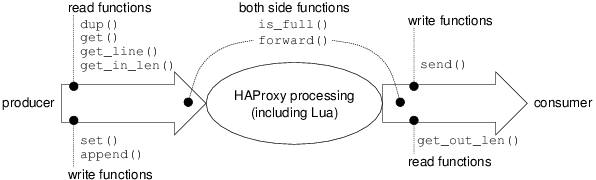
-
Channel.dup(channel)¶ This function returns a string that contain the entire buffer. The data is not remove from the buffer and can be reprocessed later.
If the buffer cant receive more data, a ‘nil’ value is returned.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
- Returns
a string containing all the available data or nil.
-
Channel.get(channel)¶ This function returns a string that contain the entire buffer. The data is consumed from the buffer.
If the buffer cant receive more data, a ‘nil’ value is returned.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
- Returns
a string containing all the available data or nil.
-
Channel.getline(channel)¶ This function returns a string that contain the first line of the buffer. The data is consumed. If the data returned doesn’t contains a final ‘n’ its assumed than its the last available data in the buffer.
If the buffer cant receive more data, a ‘nil’ value is returned.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
- Returns
a string containing the available line or nil.
-
Channel.set(channel, string)¶ This function replace the content of the buffer by the string. The function returns the copied length, otherwise, it returns -1.
The data set with this function are not send. They wait for the end of HAProxy processing, so the buffer can be full.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
string (string) – The data which will sent.
- Returns
an integer containing the amount of bytes copied or -1.
-
Channel.append(channel, string)¶ This function append the string argument to the content of the buffer. The function returns the copied length, otherwise, it returns -1.
The data set with this function are not send. They wait for the end of HAProxy processing, so the buffer can be full.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
string (string) – The data which will sent.
- Returns
an integer containing the amount of bytes copied or -1.
-
Channel.send(channel, string)¶ This function required immediate send of the data. Unless if the connection is close, the buffer is regularly flushed and all the string can be sent.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
string (string) – The data which will sent.
- Returns
an integer containing the amount of bytes copied or -1.
-
Channel.get_in_length(channel)¶ This function returns the length of the input part of the buffer.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
- Returns
an integer containing the amount of available bytes.
-
Channel.get_out_length(channel)¶ This function returns the length of the output part of the buffer.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
- Returns
an integer containing the amount of available bytes.
-
Channel.forward(channel, int)¶ This function transfer bytes from the input part of the buffer to the output part.
- Arguments
channel (class_channel) – The manipulated Channel.
int (integer) – The amount of data which will be forwarded.
-
Channel.is_full(channel)¶ This function returns true if the buffer channel is full.
- Returns
a boolean
HTTP class¶
-
class
HTTP()¶ This class contain all the HTTP manipulation functions.
-
HTTP.req_get_headers(http)¶ Returns a table containing all the request headers.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
- Returns
table of headers.
- See
This is the form of the returned table:
HTTP:req_get_headers()['<header-name>'][<header-index>] = "<header-value>"
local hdr = HTTP:req_get_headers()
hdr["host"][0] = "www.test.com"
hdr["accept"][0] = "audio/basic q=1"
hdr["accept"][1] = "audio/*, q=0.2"
hdr["accept"][2] = "*/*, q=0.1"
-
HTTP.res_get_headers(http)¶ Returns a table containing all the response headers.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
- Returns
table of headers.
- See
This is the form of the returned table:
HTTP:res_get_headers()['<header-name>'][<header-index>] = "<header-value>"
local hdr = HTTP:req_get_headers()
hdr["host"][0] = "www.test.com"
hdr["accept"][0] = "audio/basic q=1"
hdr["accept"][1] = "audio/*, q=0.2"
hdr["accept"][2] = "*.*, q=0.1"
-
HTTP.req_add_header(http, name, value)¶ Appends an HTTP header field in the request whose name is specified in “name” and whose value is defined in “value”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
value (string) – The header value.
- See
-
HTTP.res_add_header(http, name, value)¶ Appends an HTTP header field in the response whose name is specified in “name” and whose value is defined in “value”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
value (string) – The header value.
- See
-
HTTP.req_del_header(http, name)¶ Removes all HTTP header fields in the request whose name is specified in “name”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
- See
-
HTTP.res_del_header(http, name)¶ Removes all HTTP header fields in the response whose name is specified in “name”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
- See
-
HTTP.req_set_header(http, name, value)¶ This variable replace all occurrence of all header “name”, by only one containing the “value”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
value (string) – The header value.
- See
This function does the same work as the following code:
function fcn(txn)
TXN.http:req_del_header("header")
TXN.http:req_add_header("header", "value")
end
-
HTTP.res_set_header(http, name, value)¶ This variable replace all occurrence of all header “name”, by only one containing the “value”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
value (string) – The header value.
- See
-
HTTP.req_rep_header(http, name, regex, replace)¶ Matches the regular expression in all occurrences of header field “name” according to “regex”, and replaces them with the “replace” argument. The replacement value can contain back references like 1, 2, … This function works with the request.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
regex (string) – The match regular expression.
replace (string) – The replacement value.
- See
-
HTTP.res_rep_header(http, name, regex, string)¶ Matches the regular expression in all occurrences of header field “name” according to “regex”, and replaces them with the “replace” argument. The replacement value can contain back references like 1, 2, … This function works with the request.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
name (string) – The header name.
regex (string) – The match regular expression.
replace (string) – The replacement value.
- See
-
HTTP.req_set_method(http, method)¶ Rewrites the request method with the parameter “method”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
method (string) – The new method.
-
HTTP.req_set_path(http, path)¶ Rewrites the request path with the “path” parameter.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
path (string) – The new path.
-
HTTP.req_set_query(http, query)¶ Rewrites the request’s query string which appears after the first question mark (“?”) with the parameter “query”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
query (string) – The new query.
-
HTTP.req_set_uri(http, uri)¶ Rewrites the request URI with the parameter “uri”.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
uri (string) – The new uri.
-
HTTP.res_set_status(http, status[, reason])¶ Rewrites the response status code with the parameter “code”.
If no custom reason is provided, it will be generated from the status.
- Arguments
http (class_http) – The related http object.
status (integer) – The new response status code.
reason (string) – The new response reason (optional).
TXN class¶
-
class
TXN()¶ The txn class contain all the functions relative to the http or tcp transaction (Note than a tcp stream is the same than a tcp transaction, but an HTTP transaction is not the same than a tcp stream).
The usage of this class permits to retrieve data from the requests, alter it and forward it.
All the functions provided by this class are available in the context sample-fetches and actions.
-
TXN.c¶ - Returns
An Converters class.
This attribute contains a Converters class object.
-
TXN.sc¶ - Returns
An Converters class.
This attribute contains a Converters class object. The functions of this object returns always a string.
-
TXN.f¶ - Returns
An Fetches class.
This attribute contains a Fetches class object.
-
TXN.sf¶ - Returns
An Fetches class.
This attribute contains a Fetches class object. The functions of this object returns always a string.
-
TXN.req¶ - Returns
An Channel class.
This attribute contains a channel class object for the request buffer.
-
TXN.res¶ - Returns
An Channel class.
This attribute contains a channel class object for the response buffer.
-
TXN.http¶ - Returns
An HTTP class.
This attribute contains an HTTP class object. It is available only if the proxy has the “mode http” enabled.
-
TXN.log(TXN, loglevel, msg)¶ This function sends a log. The log is sent, according with the HAProxy configuration file, on the default syslog server if it is configured and on the stderr if it is allowed.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
loglevel (integer) – Is the log level associated with the message. It is a number between 0 and 7.
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
core.emerg,core.alert,core.crit,core.err,core.warning,core.notice,core.info,core.debug(log level definitions)- See
- See
- See
- See
- See
-
TXN.deflog(TXN, msg)¶ Sends a log line with the default loglevel for the proxy associated with the transaction.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
:js:func:`TXN.log
-
TXN.Debug(txn, msg)¶ - Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
Does the same job than:
function Debug(txn, msg)
TXN.log(txn, core.debug, msg)
end
-
TXN.Info(txn, msg)¶ - Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
function Debug(txn, msg)
TXN.log(txn, core.info, msg)
end
-
TXN.Warning(txn, msg)¶ - Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
function Debug(txn, msg)
TXN.log(txn, core.warning, msg)
end
-
TXN.Alert(txn, msg)¶ - Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
msg (string) – The log content.
- See
function Debug(txn, msg)
TXN.log(txn, core.alert, msg)
end
-
TXN.get_priv(txn)¶ Return Lua data stored in the current transaction (with the TXN.set_priv()) function. If no data are stored, it returns a nil value.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
- Returns
the opaque data previously stored, or nil if nothing is available.
-
TXN.set_priv(txn, data)¶ Store any data in the current HAProxy transaction. This action replace the old stored data.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
data (opaque) – The data which is stored in the transaction.
-
TXN.set_var(TXN, var, value)¶ Converts a Lua type in a HAProxy type and store it in a variable <var>.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
value (type) – The value associated to the variable. The type can be string or integer.
-
TXN.unset_var(TXN, var)¶ Unset the variable <var>.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
-
TXN.get_var(TXN, var)¶ Returns data stored in the variable <var> converter in Lua type.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
-
TXN.done(txn)¶ This function terminates processing of the transaction and the associated session. It can be used when a critical error is detected or to terminate processing after some data have been returned to the client (eg: a redirect).
Warning: It not make sense to call this function from sample-fetches. In this case the behaviour of this one is the same than core.done(): it quit the Lua execution. The transaction is really aborted only from an action registered function.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
-
TXN.set_loglevel(txn, loglevel)¶ Is used to change the log level of the current request. The “loglevel” must be an integer between 0 and 7.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
loglevel (integer) – The required log level. This variable can be one of
- See
core.emerg,core.alert,core.crit,core.err,core.warning,core.notice,core.info,core.debug(log level definitions)
-
TXN.set_tos(txn, tos)¶ Is used to set the TOS or DSCP field value of packets sent to the client to the value passed in “tos” on platforms which support this.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
tos (integer) – The new TOS os DSCP.
-
TXN.set_mark(txn, mark)¶ Is used to set the Netfilter MARK on all packets sent to the client to the value passed in “mark” on platforms which support it.
- Arguments
txn (class_txn) – The class txn object containing the data.
mark (integer) – The mark value.
Socket class¶
-
class
Socket()¶ This class must be compatible with the Lua Socket class. Only the ‘client’ functions are available. See the Lua Socket documentation:
-
Socket.close(socket)¶ Closes a TCP object. The internal socket used by the object is closed and the local address to which the object was bound is made available to other applications. No further operations (except for further calls to the close method) are allowed on a closed Socket.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
Note: It is important to close all used sockets once they are not needed, since, in many systems, each socket uses a file descriptor, which are limited system resources. Garbage-collected objects are automatically closed before destruction, though.
-
Socket.connect(socket, address[, port])¶ Attempts to connect a socket object to a remote host.
In case of error, the method returns nil followed by a string describing the error. In case of success, the method returns 1.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
address (string) – can be an IP address or a host name. See below for more information.
port (integer) – must be an integer number in the range [1..64K].
- Returns
1 or nil.
An address field extension permits to use the connect() function to connect to other stream than TCP. The syntax containing a simpleipv4 or ipv6 address is the basically expected format. This format requires the port.
Other format accepted are a socket path like “/socket/path”, it permits to connect to a socket. Abstract namespaces are supported with the prefix “abns@”, and finally a file descriptor can be passed with the prefix “fd@”. The prefix “ipv4@”, “ipv6@” and “unix@” are also supported. The port can be passed int the string. The syntax “127.0.0.1:1234” is valid. In this case, the parameter port must not be set.
-
Socket.connect_ssl(socket, address, port)¶ Same behavior than the function socket:connect, but uses SSL.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
- Returns
1 or nil.
-
Socket.getpeername(socket)¶ Returns information about the remote side of a connected client object.
Returns a string with the IP address of the peer, followed by the port number that peer is using for the connection. In case of error, the method returns nil.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
- Returns
a string containing the server information.
-
Socket.getsockname(socket)¶ Returns the local address information associated to the object.
The method returns a string with local IP address and a number with the port. In case of error, the method returns nil.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
- Returns
a string containing the client information.
-
Socket.receive(socket[, pattern[, prefix]])¶ Reads data from a client object, according to the specified read pattern. Patterns follow the Lua file I/O format, and the difference in performance between all patterns is negligible.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
pattern (string|integer) – Describe what is required (see below).
prefix (string) – A string which will be prefix the returned data.
- Returns
a string containing the required data or nil.
Pattern can be any of the following:
- `*a`: reads from the socket until the connection is closed. No
end-of-line translation is performed;
- `*l`: reads a line of text from the Socket. The line is terminated by a
LF character (ASCII 10), optionally preceded by a CR character (ASCII 13). The CR and LF characters are not included in the returned line. In fact, all CR characters are ignored by the pattern. This is the default pattern.
- number: causes the method to read a specified number of bytes from the
Socket. Prefix is an optional string to be concatenated to the beginning of any received data before return.
empty: If the pattern is left empty, the default option is *l.
If successful, the method returns the received pattern. In case of error, the method returns nil followed by an error message which can be the string ‘closed’ in case the connection was closed before the transmission was completed or the string ‘timeout’ in case there was a timeout during the operation. Also, after the error message, the function returns the partial result of the transmission.
Important note: This function was changed severely. It used to support multiple patterns (but I have never seen this feature used) and now it doesn’t anymore. Partial results used to be returned in the same way as successful results. This last feature violated the idea that all functions should return nil on error. Thus it was changed too.
-
Socket.send(socket, data[, start[, end]])¶ Sends data through client object.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
data (string) – The data that will be sent.
start (integer) – The start position in the buffer of the data which will be sent.
end (integer) – The end position in the buffer of the data which will be sent.
- Returns
see below.
Data is the string to be sent. The optional arguments i and j work exactly like the standard string.sub Lua function to allow the selection of a substring to be sent.
If successful, the method returns the index of the last byte within [start, end] that has been sent. Notice that, if start is 1 or absent, this is effectively the total number of bytes sent. In case of error, the method returns nil, followed by an error message, followed by the index of the last byte within [start, end] that has been sent. You might want to try again from the byte following that. The error message can be ‘closed’ in case the connection was closed before the transmission was completed or the string ‘timeout’ in case there was a timeout during the operation.
Note: Output is not buffered. For small strings, it is always better to concatenate them in Lua (with the ‘..’ operator) and send the result in one call instead of calling the method several times.
-
Socket.setoption(socket, option[, value])¶ Just implemented for compatibility, this cal does nothing.
-
Socket.settimeout(socket, value[, mode])¶ Changes the timeout values for the object. All I/O operations are blocking. That is, any call to the methods send, receive, and accept will block indefinitely, until the operation completes. The settimeout method defines a limit on the amount of time the I/O methods can block. When a timeout time has elapsed, the affected methods give up and fail with an error code.
The amount of time to wait is specified as the value parameter, in seconds.
The timeout modes are bot implemented, the only settable timeout is the inactivity time waiting for complete the internal buffer send or waiting for receive data.
- Arguments
socket (class_socket) – Is the manipulated Socket.
value (integer) – The timeout value. Use floating point to specify milliseconds.
Regex class¶
-
class
Regex()¶ This class allows the usage of HAProxy regexes because classic lua doesn’t provides regexes. This class inherits the HAProxy compilation options, so the regexes can be libc regex, pcre regex or pcre JIT regex.
The expression matching number is limited to 20 per regex. The only available option is case sensitive.
Because regexes compilation is a heavy process, it is better to define all your regexes in the body context and use it during the runtime.
-- Create the regex
st, regex = Regex.new("needle (..) (...)", true);
-- Check compilation errors
if st == false then
print "error: " .. regex
end
-- Match the regexes
print(regex:exec("Looking for a needle in the haystack")) -- true
print(regex:exec("Lokking for a cat in the haystack")) -- false
-- Extract words
st, list = regex:match("Looking for a needle in the haystack")
print(st) -- true
print(list[1]) -- needle in the
print(list[2]) -- in
print(list[3]) -- the
-
Regex.new(regex, case_sensitive)¶ Create and compile a regex.
- Arguments
regex (string) – The regular expression according with the libc or pcre standard
case_sensitive (boolean) – Match is case sensitive or not.
- Returns
boolean status and Regex class or string containing fail reason.
-
Regex.exec(regex, str)¶ Execute the regex.
- Arguments
regex (class_regex) – A Regex class object.
str (string) – The input string will be compared with the compiled regex.
- Returns
a boolean status according with the match result.
-
Regex.match(regex, str)¶ Execute the regex and return matched expressions.
- Arguments
map (class_map) – A Regex class object.
str (string) – The input string will be compared with the compiled regex.
- Returns
a boolean status according with the match result, and a table containing all the string matched in order of declaration.
Map class¶
-
class
Map()¶ This class permits to do some lookup in HAProxy maps. The declared maps can be modified during the runtime through the HAProxy management socket.
default = "usa"
-- Create and load map
geo = Map.new("geo.map", Map._ip);
-- Create new fetch that returns the user country
core.register_fetches("country", function(txn)
local src;
local loc;
src = txn.f:fhdr("x-forwarded-for");
if (src == nil) then
src = txn.f:src()
if (src == nil) then
return default;
end
end
-- Perform lookup
loc = geo:lookup(src);
if (loc == nil) then
return default;
end
return loc;
end);
-
Map._int¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.intis also available for compatibility.
-
Map._ip¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.ipis also available for compatibility.
-
Map._str¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.stris also available for compatibility.
-
Map._beg¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.begis also available for compatibility.
-
Map._sub¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.subis also available for compatibility.
-
Map._dir¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.diris also available for compatibility.
-
Map._dom¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.domis also available for compatibility.
-
Map._end¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
-
Map._reg¶ See the HAProxy configuration.txt file, chapter “Using ACLs and fetching samples” ans subchapter “ACL basics” to understand this pattern matching method.
Note that
Map.regis also available for compatibility.
-
Map.new(file, method)¶ Creates and load a map.
-
Map.lookup(map, str)¶ Perform a lookup in a map.
- Arguments
map (class_map) – Is the class Map object.
str (string) – Is the string used as key.
- Returns
a string containing the result or nil if no match.
-
Map.slookup(map, str)¶ Perform a lookup in a map.
- Arguments
map (class_map) – Is the class Map object.
str (string) – Is the string used as key.
- Returns
a string containing the result or empty string if no match.
AppletHTTP class¶
-
class
AppletHTTP()¶ This class is used with applets that requires the ‘http’ mode. The http applet can be registered with the core.register_service() function. They are used for processing an http request like a server in back of HAProxy.
This is an hello world sample code:
core.register_service("hello-world", "http", function(applet)
local response = "Hello World !"
applet:set_status(200)
applet:add_header("content-length", string.len(response))
applet:add_header("content-type", "text/plain")
applet:start_response()
applet:send(response)
end)
-
AppletHTTP.c¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Converters class object.
-
AppletHTTP.sc¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Converters class object. The functions of this object returns always a string.
-
AppletHTTP.f¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Fetches class object. Note that the applet execution place cannot access to a valid HAProxy core HTTP transaction, so some sample fetches related to the HTTP dependant values (hdr, path, …) are not available.
-
AppletHTTP.sf¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Fetches class object. The functions of this object returns always a string. Note that the applet execution place cannot access to a valid HAProxy core HTTP transaction, so some sample fetches related to the HTTP dependant values (hdr, path, …) are not available.
-
AppletHTTP.method¶ - Returns
string
The attribute method returns a string containing the HTTP method.
-
AppletHTTP.version¶ - Returns
string
The attribute version, returns a string containing the HTTP request version.
-
AppletHTTP.path¶ - Returns
string
The attribute path returns a string containing the HTTP request path.
-
AppletHTTP.qs¶ - Returns
string
The attribute qs returns a string containing the HTTP request query string.
-
AppletHTTP.length¶ - Returns
integer
The attribute length returns an integer containing the HTTP body length.
-
AppletHTTP.headers¶ - Returns
table
The attribute headers returns a table containing the HTTP headers. The header names are always in lower case. As the header name can be encountered more than once in each request, the value is indexed with 0 as first index value. The table have this form:
AppletHTTP.headers['<header-name>'][<header-index>] = "<header-value>"
AppletHTTP.headers["host"][0] = "www.test.com"
AppletHTTP.headers["accept"][0] = "audio/basic q=1"
AppletHTTP.headers["accept"][1] = "audio/*, q=0.2"
AppletHTTP.headers["accept"][2] = "*/*, q=0.1"
-
AppletHTTP.set_status(applet, code[, reason])¶ This function sets the HTTP status code for the response. The allowed code are from 100 to 599.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
code (integer) – the status code returned to the client.
reason (string) – the status reason returned to the client (optional).
-
AppletHTTP.add_header(applet, name, value)¶ This function add an header in the response. Duplicated headers are not collapsed. The special header content-length is used to determinate the response length. If it not exists, a transfer-encoding: chunked is set, and all the write from the funcion AppletHTTP:send() become a chunk.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
name (string) – the header name
value (string) – the header value
-
AppletHTTP.start_response(applet)¶ This function indicates to the HTTP engine that it can process and send the response headers. After this called we cannot add headers to the response; We cannot use the AppletHTTP:send() function if the AppletHTTP:start_response() is not called.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
-
AppletHTTP.getline(applet)¶ This function returns a string containing one line from the http body. If the data returned doesn’t contains a final ‘\n’ its assumed than its the last available data before the end of stream.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
- Returns
a string. The string can be empty if we reach the end of the stream.
-
AppletHTTP.receive(applet[, size])¶ Reads data from the HTTP body, according to the specified read size. If the size is missing, the function tries to read all the content of the stream until the end. If the size is bigger than the http body, it returns the amount of data available.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
size (integer) – the required read size.
- Returns
always return a string,the string can be empty is the connexion is closed.
-
AppletHTTP.send(applet, msg)¶ Send the message msg on the http request body.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
msg (string) – the message to send.
-
AppletHTTP.get_priv(applet)¶ Return Lua data stored in the current transaction. If no data are stored, it returns a nil value.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
- Returns
the opaque data previously stored, or nil if nothing is available.
- See
-
AppletHTTP.set_priv(applet, data)¶ Store any data in the current HAProxy transaction. This action replace the old stored data.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
data (opaque) – The data which is stored in the transaction.
- See
-
AppletHTTP.set_var(applet, var, value)¶ Converts a Lua type in a HAProxy type and store it in a variable <var>.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
value (type) – The value associated to the variable. The type ca be string or integer.
- See
- See
-
AppletHTTP.unset_var(applet, var)¶ Unset the variable <var>.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
- See
- See
-
AppletHTTP.get_var(applet, var)¶ Returns data stored in the variable <var> converter in Lua type.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletHTTP) – An AppletHTTP class
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
- See
- See
AppletTCP class¶
-
class
AppletTCP()¶ This class is used with applets that requires the ‘tcp’ mode. The tcp applet can be registered with the core.register_service() function. They are used for processing a tcp stream like a server in back of HAProxy.
-
AppletTCP.c¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Converters class object.
-
AppletTCP.sc¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Converters class object. The functions of this object returns always a string.
-
AppletTCP.f¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Fetches class object.
-
AppletTCP.sf¶ - Returns
This attribute contains a Fetches class object.
-
AppletTCP.getline(applet)¶ This function returns a string containing one line from the stream. If the data returned doesn’t contains a final ‘\n’ its assumed than its the last available data before the end of stream.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
- Returns
a string. The string can be empty if we reach the end of the stream.
-
AppletTCP.receive(applet[, size])¶ Reads data from the TCP stream, according to the specified read size. If the size is missing, the function tries to read all the content of the stream until the end.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
size (integer) – the required read size.
- Returns
always return a string,the string can be empty is the connexion is closed.
-
AppletTCP.send(appletmsg)¶ Send the message on the stream.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
msg (string) – the message to send.
-
AppletTCP.get_priv(applet)¶ Return Lua data stored in the current transaction. If no data are stored, it returns a nil value.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
- Returns
the opaque data previously stored, or nil if nothing is available.
- See
-
AppletTCP.set_priv(applet, data)¶ Store any data in the current HAProxy transaction. This action replace the old stored data.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
data (opaque) – The data which is stored in the transaction.
- See
-
AppletTCP.set_var(applet, var, value)¶ Converts a Lua type in a HAProxy type and stores it in a variable <var>.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
value (type) – The value associated to the variable. The type can be string or integer.
- See
- See
-
AppletTCP.unset_var(applet, var)¶ Unsets the variable <var>.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
- See
- See
-
AppletTCP.get_var(applet, var)¶ Returns data stored in the variable <var> converter in Lua type.
- Arguments
applet (class_AppletTCP) – An AppletTCP class
var (string) – The variable name according with the HAProxy variable syntax.
- See
- See
External Lua libraries¶
A lot of useful lua libraries can be found here:
Redis acces:
This is an example about the usage of the Redis library with HAProxy. Note that each call of any function of this library can throw an error if the socket connection fails.
-- load the redis library
local redis = require("redis");
function do_something(txn)
-- create and connect new tcp socket
local tcp = core.tcp();
tcp:settimeout(1);
tcp:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379);
-- use the redis library with this new socket
local client = redis.connect({socket=tcp});
client:ping();
end
OpenSSL: